Why Do You Have Toothache?
Toothache is a painful sensation from a tooth and it surrounding gum. However, it does not tell you what is actually causing the pain and there are many possible causes. The affected tooth may feel sore, pain or weak on biting normal or slightly harder food.
The toothache can change in frequency and intensity. Starting as low-grade, localised ache or vague pain lasting few seconds to few minutes mild, localised to the area of the affected tooth, when triggered by eating or drinking. As it increases in severity, the pain become more severe, throbbing and starts to spreading to a wider region, lasting few hours or even days.
A full-blown toothache is one of the most painful experience and lead to severe pain not only restricted to the mouth but to the upper and lower jaws and headaches with sleepless nights.


Sensitivities to hot/cold food and drinks is usually the first symptoms that the tooth is having trouble.
The common causes for this unpleasant sensation is due to excessive hard and aggressive brushing that forces the gum to recede and expose the sensitive portion of the roots to changes in temperature in our food/drinks.
Other causes of tooth sensitivity are tooth decay, dislodged fillings, gum diseases and cracked tooth.

The exposed root surfaces is not cover by the protective layer of the gum, thus allowing the root to come in direct contact with temperature changes of food/drinks or acidic or sweet substances like orange juices.
First, stopping this problem must start with a change of brushing habits with light, gentle forces and correct toothbrush with fine, soft bristles.
Then the exposed part of the teeth can be easily repaired with a tooth colour fillings to prevent the direct contact of the sensitive roots with thermal stimulation and also to protect the roots from further wearing down during tooth brushing.
However, the gum that has been pushed away due to the forceful tooth brushing will not grow back, so the teeth will long longer than usual.
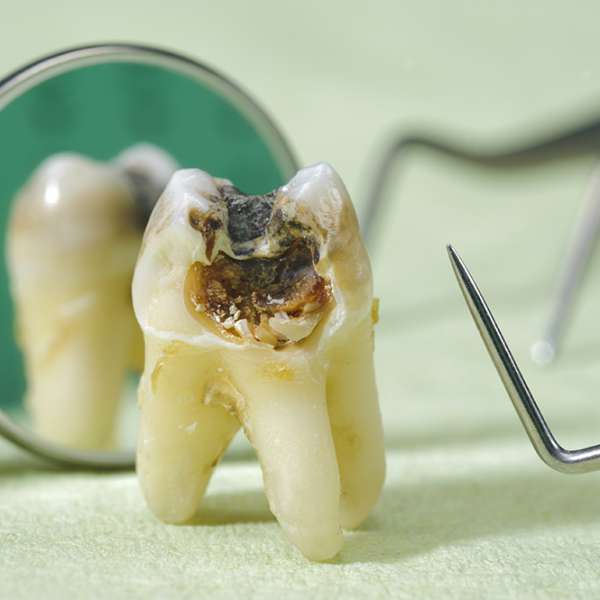

Tooth decay, caries or cavities are caused by the bacterial plaque which is a layer of germs (bacteria) covering all the exposed surfaces of your teeth in the mouth.
If the plaque is allowed to stayed on the surface of the teeth over a prolonged time, these germs will release acid as waste products that will soften the tooth structure.
As the area of softening caused by the acid attack enlarges, it will become structurally weak and collapse under the pressure of chewing to create holes or cavities on the teeth.
The tooth is covered by a harder, outer layer of enamel and softer, inner layer of dentin. Any holes on the enamel layer will not cause any pain as this layer is a non-living structure.
If this acid attack continues, and the holes not fixed, more weakened tooth structure will fracture away to create larger holes.
As the holes enlarges, the bacterial plaque penetrates through the enamel and reaches the dentin and pain (in the form of sensitivity) will be felt as this hard structure is populated with living cells.
Pain is a warning sign of the body informing us that something is wrong or injured.
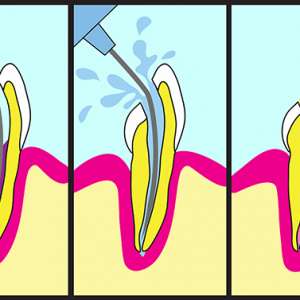
If this pain is ignored, the holes get deeper into the nerve (pulp) of the tooth, the bacterial attack on the nerve will cause permanent inflammation and infection leading to an extremely painful, full-blown toothache that result in the death of the pulp of the tooth (dead tooth).
The only solutions for dealing with a dead tooth is to either do a root canal treatment to save it or to extract the infected tooth out.

Symptoms include sensitivity to hot/cold while the nerve of the tooth is injured and dying. Most time, it will develop into full-blown toothache with severe throbbing pain.
Occasionally, the dying tooth may just die silently and only presented with a small pimple like lump on the gum beside the root of the tooth which discharges pus, without much pain and only to flare up in the future when the patient’s immunity is low.
The treatment of dead tooth is either save it with a root canal treatment or to extract it.
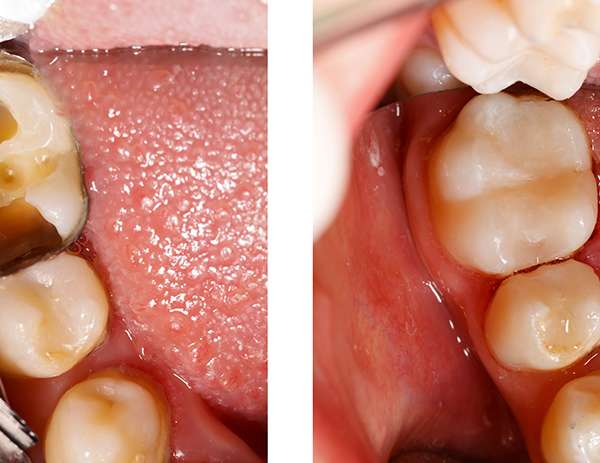

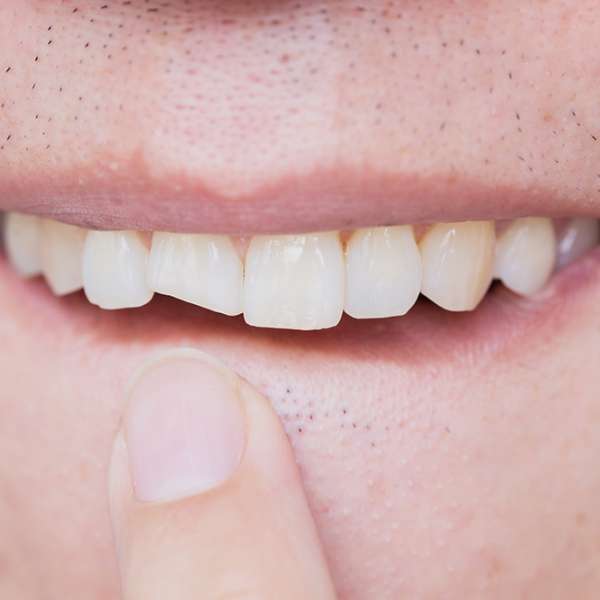
Cracked tooth due to fractured caused by persistent tooth grinding or clenching at night or tooth with deep and large fillings may also result in infection of tooth as bacteria can seep through the micro-cracks and cause the nerve to die.
Sometimes, the cracked tooth literally split into 2 or more pieces under the forces of biting.
Whether a cracked tooth can be saved depends on the severity and direction of the crack, the health of the pulp (nerve of the tooth) and the health of the gum and surrounding bone.
Treatment of cracked tooth may be just a filling, crown, root canal treatment or extraction if it cannot be saved.
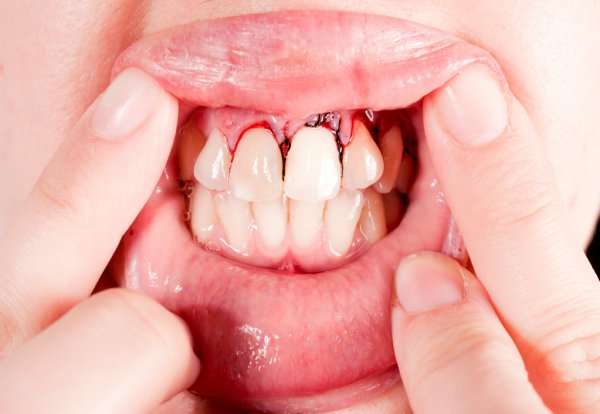

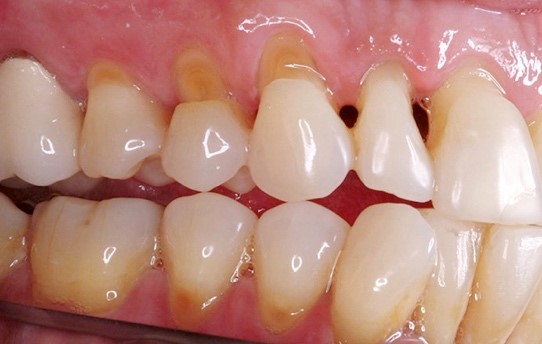
Gum disease is the most common form of gum pain as the bacterial plaque destroy the supporting gum and bone of the teeth.
It may start as mild sensitivity to hot/cold as the destroyed gum begin to expose the roots and also bleeding gum during brushing.
The infected tooth may feel weak or loose when biting and start to shift it position from the adjacent teeth. Pus may form creating “gum boils”.
As the gum disease increases in severity, more destruction of the bone and gum leads to more pain, mobility and looseness of the tooth to the extent that it will need to be extracted and even fall out by itself.
Early stage of gum disease is reversible and treatable while in more severe and later stage of gum disease will lead to permanent destruction of surrounding gum and bone.
The treatment depending on the severity of the gum disease.
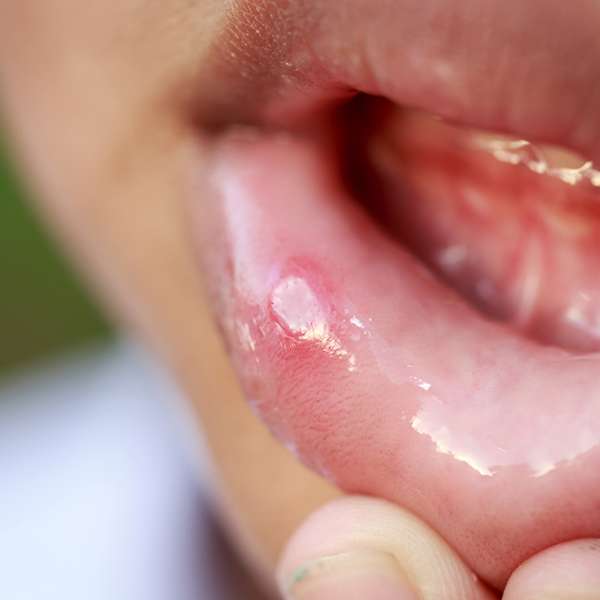

Another common cause of gum pain is mouth ulcer of the gum or other part of the mouth like the cheek, lip, gum, palate, tongue and floor of tongue.
Most of these ulcers has unknown origin called Apthous ulcer or cranker sore, or can also be of traumatic or infective in nature.
More dangerous form of ulcer that does not heal for a period of more than 2 weeks may be sign of mouth cancers.
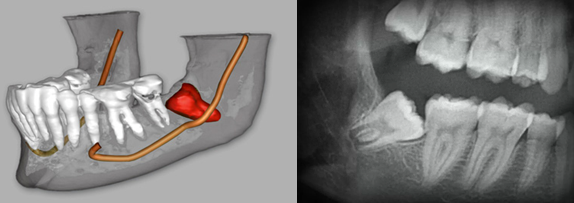

Sometimes the wisdom tooth is crooked (impacted), facing towards the adjacent tooth in front instead of erupting in an upright position, the gum covering the partially erupted wisdom tooth become infected by the food trap and bacterial plaque.
This persistent food trap will gradually lead to gum disease and tooth decay on the wisdom tooth itself, or worse compromising the health of the tooth in front of it.
Thus it is highly recommended to remove crooked wisdom tooth with food trap to save the healthy, straight tooth in front of it.
Young children may experience the same pain during tooth eruption of baby teeth as the new tooth forces its way out of the gum. During change of milk teeth, the child may feel some gum pain as the shaky tooth irritate the gum when forces is applied to it during chewing.
This discomfort can be treated with application of teething gel to relieve the pain on the gum or removal of the shaky milk tooth.

Pain around the teeth and the jaws can be symptoms of heart disease such as angina.
If our dentist suspects a medical illness could be the cause of your toothache, he or she may refer you to a medical doctor.
Why Do You Need to Fix Your Toothache?
You should see our dentist as soon as possible when you experience a toothache. A toothache can typically affect your daily life. It can affect your mood, your work performance, your ability to carry out daily activities, your quality of sleep and your social relationship.
In a rare, worst case scenario, a toothache that is caused by an infection and left untreated, can be life-threatening. The types of treatment required for toothache depends on the causes and the amount of damaged done to the tooth and its surrounding tissue.
Our dentist will diagnose the cause of your pain and will explain to you in details what treatment options you have, the time and cost needed, and the prognosis of success before proceeding with any treatment. This can lead to deterioration of the remaining teeth.
Fortunately, there are several options for replacing missing teeth. During a consultation with our dentists, you can learn more about your specific tooth loss problem and the treatment options. Most importantly is to break this cycle of self-destruction as the numbers of teeth get fewer in the mouth by saving whatever teeth that are left behind. Hopeless teeth will need to be removed and teeth with better chances of survival will be saved.
Implants, bridges and dentures are all possible solutions to replace your missing teeth that will restore your chewing ability and gain back your confidence.
Our Approach
The tooth is removed with the help of dental instrument and the tooth usually can be removed as a single piece.
It removes the source of infection from within the pulp chamber of the tooth.